仅记录API调用,防忘笔记
Spring框架下服务端返回JSON数据也是比以前方便很多的,不需要去处理JSON对象&JSON数组&JSON字符串这些以前要处理的乱七八糟的东西,基本只需要建好相应类,直接映射就好了(包括传入也是),主要工作有两步:设置Header属性content-type,一般设为”application/json;charset=utf-8”,和前端对应。可以有两种方法实现(本质一样):
返回JSON数据
一、设置注解
通过在@RequestMapping方法上加上@ResponseBody注解(若类为RestController则默认所有方法都自动添加了),接着在修改@RequestMapping为@RequestMapping(value = <myUri>, produces = "application/json;charset=UTF-8"),这行代码即设置了返回类型,然后直接返回对象即可,代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
@RequestMapping(value = "/uri", produces = "application/json;charset=UTF-8")
public QueryResult<UserOutputDTO> login(@RequestBody LoginCommandDTO loginCommand, HttpServletRequest request) {
//..
return queryResult;
}
这样子返回的默认就是类的属性名加上值的形式了,类中的List,Set会自动转为JSON中的数组。 若要自定义JSON的key名,可以在返回的类中加上注解: @JsonProperty:可以自定义属性标签名字(序列化/反序列化均可,对应返回/获取数据,仅可设置一个代替属性名,原来的失效); @JsonAlias:自定义可以接收的属性标签名字(仅用于反序列化时可以接收的名字,可以有多个名字,肯定包括了@JsonProperty中设置的或属性名),@JsonAlias注解需要依赖于setter、getter,而@JsonProperty注解不需要。; @JsonIngore:可以来忽略不想输出的某个属性的标签; @JsonInclude:可以用来动态包含属性的标签,为null值则不添加进JSON中。
如下代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
@JsonProperty(value = "user_id")
private int id;
@JsonIngore
private String phone;
//这样也可以,但建议用@JsonAlias
private byte red;
@JsonProperty("r")
public byte getR() {
return red;
}
@JsonProperty("red")
public void setRed(byte red) {
this.red = red;
}
二、直接操作HttpServletResponse
这种方法比较原始,还是需要涉及到JSON字符串转换的问题。代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
@RequestMapping(value = "/uri", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public void getUserName(@RequestBody InputDTO inputDTO, HttpServletResponse resp) {
//...
JSONObject result = new JSONObject();
result.put("name", user.name);
//设置Header
resp.setContentType("application/json;charset=UTF-8");
try {
PrintWriter out = resp.getWriter();
//转为JSON字符串并写入返回body
out.write(json.toJSONString());
out.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
if(out != null){
out.close();
}
}
}
获取数据
数据可以来自url(这里又分为path中的和query中的),来自request Header(例如获取SessionId),来自request Body(例如post方式上传JSON数据)。 那么在Controller函数就有不同的接受方法了:
来自url path
就是host/user/1这样的url, 使用@PathVariable注解,注意@RequestMapping:
1
2
3
4
5
6
@RequestMapping(value = "user/{id}")
@ResponseBody
public User login(@PathVariable int id) {
//...
return user;
}
来自request Body
- 使用@RequestBody注解 根据request Header中Content-Type的值,以下情况不可以用@RequestBody注解:
- POST方式提交时
- application/x-www-form-urlencoded,可选用@RequestParam或@ModelAttribute或@RequestBody处理(Http协议中,如果不指定Content-Type,则默认传递的参数就是application/x-www-form-urlencoded类型);
- multipart/form-data, 不能使用@RequestBody处理这种格式的数据(form表单里面有文件上传时,必须要指定enctype属性值为multipart/form-data,意思是以二进制流的形式传输文件。);
- 其他格式, 必须使用@RequestBody来处理(其他格式包括application/json, application/xml等。这些格式的数据);
- PUT方式提交时
- multipart/form-data, 不能处理;
- 其他格式, 必须;
说明:request的body部分的数据编码格式由header部分的Content-Type指定,这一转换是由spring框架来处理的,无需担心
解析json数据大体流程概述:
Http传递请求体信息,最终会被封装进com.fasterxml.jackson.core.json.UTF8StreamJsonParser中(提示:Spring采用CharacterEncodingFilter设置了默认编码为UTF-8),然后在public class BeanDeserializer extends BeanDeserializerBase implements java.io.Serializable中,通过 public Object deserializeFromObject(JsonParser p, DeserializationContext ctxt) throws IOException方法进行解析。
核心逻辑分析示例:
后端的模型只有name和age属性,以及对应的setter/getter方法;给出一般用到的deserializeFromObject(JsonParser p, DeserializationContext ctxt)方法的核心逻辑:
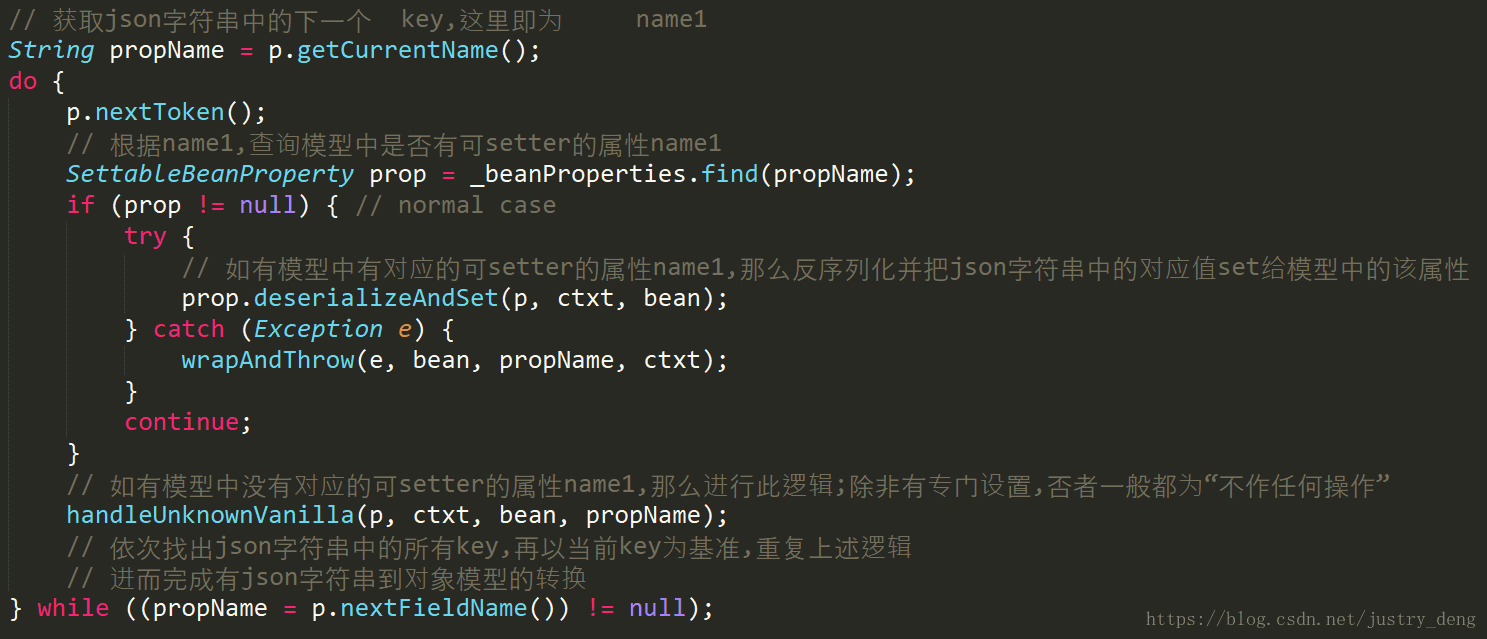
1
2
3
4
@RequestMapping(value="/requestParamTest", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String requestParamTest(@RequestBody User user){
return user.name;
}
- 使用@RequestParam注解
也可以获取到path中的query值,所以可以是GET方式。
实质:get方式中query String的值,和post方式中body data的值都会被Servlet接受到并转化到Request.getParameter()参数集中,所以@RequestParam可以获取的到。
说明:如果@RequestParam后面的参数没有被包含在提交的数据中,则会报错
1 2 3 4
@RequestMapping(value="/requestParamTest", method = RequestMethod.POST) public String requestParamTest(@RequestBody User user, @RequestParam(value="username") String name, @RequestParam(value="userId") String id){ return name; }
-
直接在方法函数中写出
这种方法使用@RequestParam的不同点在于当传入数据不包含这一项时,不是报错,而是置空。注意名称要保持一致。
1
2
3
4
@RequestMapping(value="/requestParamTest", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String requestParamTest(@RequestBody User user, String name, String id){
return name;
}
- @ModelAttribute
觉得不需要用了..毕竟这是和视图联系在一起的,但是现在前后端分离做得很好了
来自request Header
request中还有cookie等信息。代码:
1
2
3
4
@RequestMapping(value="/requestParamTest", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String requestParamTest(HttpServletRequest request){
return request.getHeader("JSESSIONID");
}